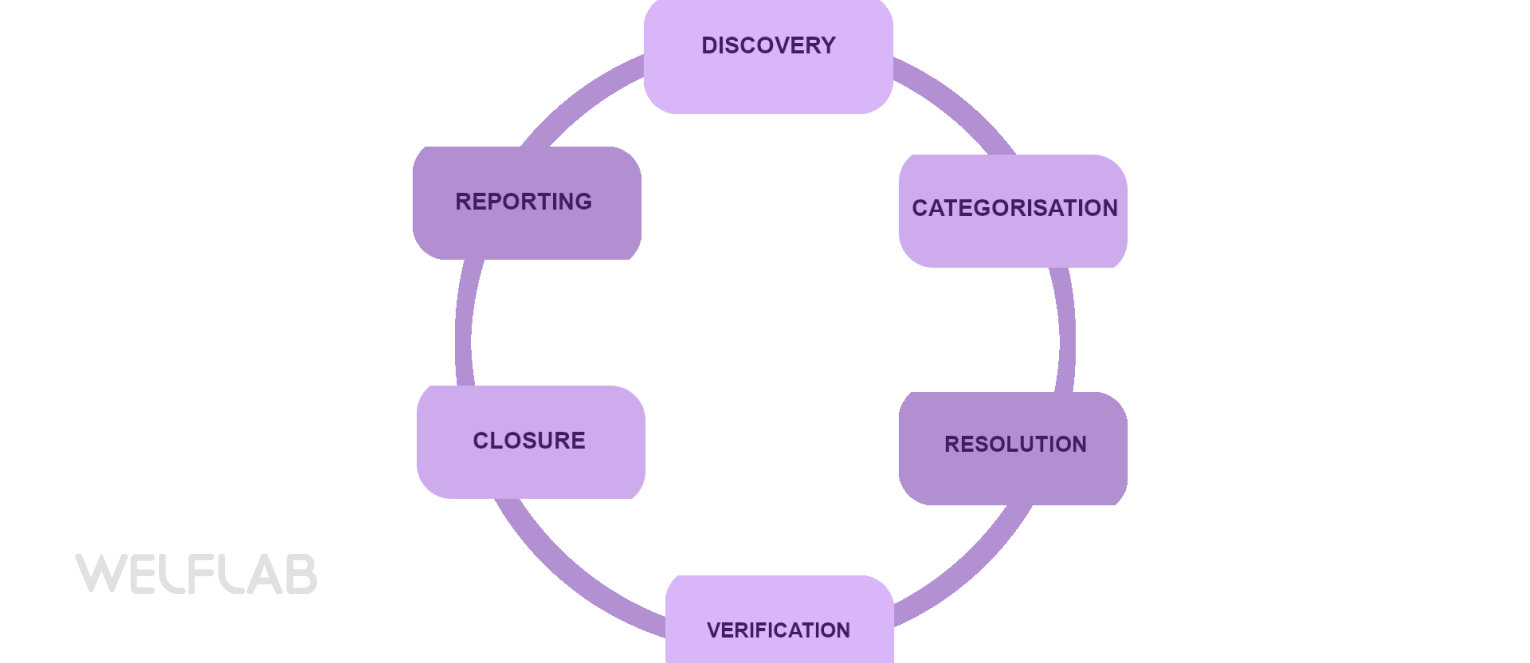
In the world of software development, defects or bugs are inevitable. These flaws can range from minor issues to critical errors that can disrupt the entire system. To ensure high-quality software, it is crucial to have an effective defect management process in place. The defect management process refers to a systematic approach used by software development teams to identify, track, analyze, and resolve defects encountered during testing or after the software’s release.
It involves various stages, including bug detection, categorization, prioritization, assignment to developers, fixing the issues, retesting, and ultimately closing them. The importance of a robust defect management process cannot be overstated. It not only helps in identifying and addressing bugs promptly but also ensures that they do not reoccur in subsequent versions or releases. By managing defects efficiently, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction as well as their reputation by delivering reliable and error-free software solutions.
Moreover, an effective defect management process facilitates collaboration among team members involved in different stages of software testing. It provides clear visibility into the status of defects and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and project timelines. This article explores the various aspects of the defect management process from bug detection to resolution.
Step 1: Bug Detection And Error Identification: How To Identify And Report Bugs Effectively
Bug detection and error identification are crucial steps in the defect management process. The early detection of bugs allows for timely resolution, minimizing the impact on software development projects. Here are some effective strategies to identify and report bugs:
- Thorough Testing: Conduct comprehensive testing of the software application or system to identify any functional or performance issues. This includes both manual testing by human testers and automated testing using specialized tools. 2. Reproduce the Bug: To ensure accuracy in bug reporting, it is essential to reproduce the bug consistently. This involves noting down step-by-step instructions on how to recreate the error, including specific inputs, conditions, or actions that trigger it.
- Detailed Bug Reports: When reporting a bug, provide a detailed description that includes specific information such as the environment (operating system, browser version), steps to reproduce the bug, expected behaviour versus actual behaviour observed, and any relevant screenshots or logs. 4. Prioritize Bugs: Assign severity levels to reported bugs based on their impact on functionality or criticality. This helps developers prioritize their efforts in resolving high-priority bugs first.
Step 2: Defect Triage And Prioritization: Streamlining The Escalation Process For Efficient Bug Resolution
Defect triage and prioritization play a crucial role in streamlining the escalation process for efficient bug resolution. Once bugs are detected, it becomes essential to categorize and prioritize them based on their severity, impact, and urgency. This step ensures that resources are allocated effectively, allowing organizations to address critical issues promptly while optimizing time and efforts. During defect triage, a cross-functional team consisting of developers, testers, project managers, and stakeholders comes together to evaluate each bug’s characteristics.
The team carefully examines factors such as the frequency of occurrence, potential impact on end-users or business processes, and its alignment with organizational goals. By collaboratively analyzing these aspects, the team can determine which defects require immediate attention. Prioritization is another key aspect of this step. By assigning a priority level to each defect based on its severity and impact, teams can focus their resources on resolving high-priority issues first.
This prevents bottlenecks in the resolution process by ensuring that critical bugs do not get lost in the shuffle. Efficient defect triage and prioritization enable organizations to streamline their bug resolution process by effectively managing limited resources.
Step 3: Bug Fixing And Resolution Workflow: From Root Cause Analysis To Successful Defect Closure
Once a bug has been detected and reported, the next crucial step in the defect management process is to fix and resolve it. This involves a systematic workflow that ensures the identification of the root cause of the bug and its subsequent resolution.
The first step in this workflow is conducting a thorough root cause analysis. This involves investigating the underlying factors that led to the occurrence of the bug. By identifying the root cause, developers can gain insights into why the defect happened, enabling them to devise an effective solution.
Following root cause analysis, developers proceed with designing and implementing a fix for the bug. This may involve modifying code, adjusting configurations, or making other necessary changes to eliminate the defect. The fixed code is then thoroughly tested to ensure that it resolves the issue without introducing new bugs or affecting existing functionalities.
Once testing is complete and satisfactory results are obtained, defect closure can take place. The resolved bug is marked as closed in the defect tracking system, indicating that it has been successfully addressed.
Proper documentation of all steps taken during this workflow is essential for future reference and knowledge sharing within development teams. Additionally, regular communication between developers and testers throughout this process helps ensure smooth coordination and timely resolution of defects.
Step 4: Continuous Improvement and Knowledge Sharing: Enhancing Quality Assurance Through Defect Prevention Strategies
Continuous improvement and knowledge sharing are vital components of the defect management process, as they enable organizations to enhance their quality assurance efforts through effective defect prevention strategies. By adopting a proactive approach, companies can minimize the occurrence of defects and improve overall product quality. One key aspect of continuous improvement is conducting regular reviews and analysis of the defect management process.
This involves evaluating the effectiveness of existing practices, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary changes. By analyzing trends in bug detection and resolution, organizations can identify patterns or common issues that lead to defects. This information is then used to develop preventive measures that address these root causes. Knowledge sharing plays a crucial role in enhancing defect prevention strategies. It involves creating a culture where information about past defects, their resolution, and preventive measures is shared across teams and departments.
Through documentation, training sessions, or collaborative platforms, employees gain access to valuable insights that help them identify potential risks early on in the development cycle. Furthermore, organizations can establish feedback loops with customers or end-users to gather insights about their experiences with defects. This feedback provides valuable input for improving product design or addressing recurring issues.
In conclusion, the defect management process is essential for high-quality software, systematically identifying and resolving bugs. The process involves bug detection, categorization, prioritization, assignment, fixing, retesting, and closure. Effective bug detection strategies include thorough testing, accurate bug reproduction, detailed reports, and prioritization.
Defect triage and prioritization streamline bug resolution by evaluating characteristics and assigning priority levels. The bug fixing workflow includes root cause analysis, code modification, testing, and closure, with documentation and communication between developers and testers.
Continuous improvement and knowledge sharing enhance quality assurance by identifying areas for improvement and fostering a culture of learning from past defects. A proactive approach and effective defect management contribute to minimizing defects and improving overall product quality.